NSI Draughtsman Syllabus 2026 – Complete Topic-wise Breakdown
Contents
✓ Verified against National Sugar Institute (NSI) Notification No. 1/2026. All topics for Written and Skill tests reproduced verbatim.
The National Sugar Institute (NSI), Kanpur, requires Draughtsmen to possess a high degree of precision in mechanical drafting and computer-aided design. The selection process involves a Skill Test (Qualifying) followed by a Written Examination (Merit-based).
Exam Pattern Overview (2026)
| Stage | Mode | Nature | Marks |
| Stage 1: Skill Test | Practical/Trade Test | Qualifying | Pass/Fail |
| Stage 2: Written Test | Objective/Subjective | Merit-Ranking | 100 Marks |
Export to Sheets
- Written Test Duration: 3 Hours.
- Skill Test: Focuses on CAD proficiency and manual drawing accuracy.
- Merit: Final selection is based solely on the Written Test score for candidates who qualify the Skill Test.
Written Examination Syllabus (Verbatim)
1. Fundamental Drawing Principles
- Nomenclature, description, and use of drawing instruments & various equipment used in drawing office. Their care and maintenance.
- Layout of a drawing sheet as per B.I.S. (Bureau of Indian Standards).
- Lines and their meanings; type of lettering, proportion, and spacing of letters and words.
- Terms & definitions: Polygons and circles.
- Definition of ellipse, parabola, hyperbola; different methods of their construction.
- Definition & method of drawing cycloid curves, helix, and spirals.
2. Projections & Geometry
- Terminology: Feature, functional feature, functional dimension, datum dimension, and principles.
- Units of dimensioning, systems of dimensioning, and methods for common features.
- Planes and their normal projections; orthographic projection (First angle and third angle).
- Projections of solids: Prisms, cones, pyramids, and frustums in various positions.
- Construction of different types of scales: Principle of R.F., diagonal, and Vernier scales.
- Sectional views: Importance, types, and parts not shown in section.
- True shape of surfaces: Solids cut by different cutting planes.
- Development of surfaces: Industrial need and methods of developing surfaces.
- Intersections & Interpenetration: Intersection of prisms, cones, pyramids, and cylinders with intersecting axes.
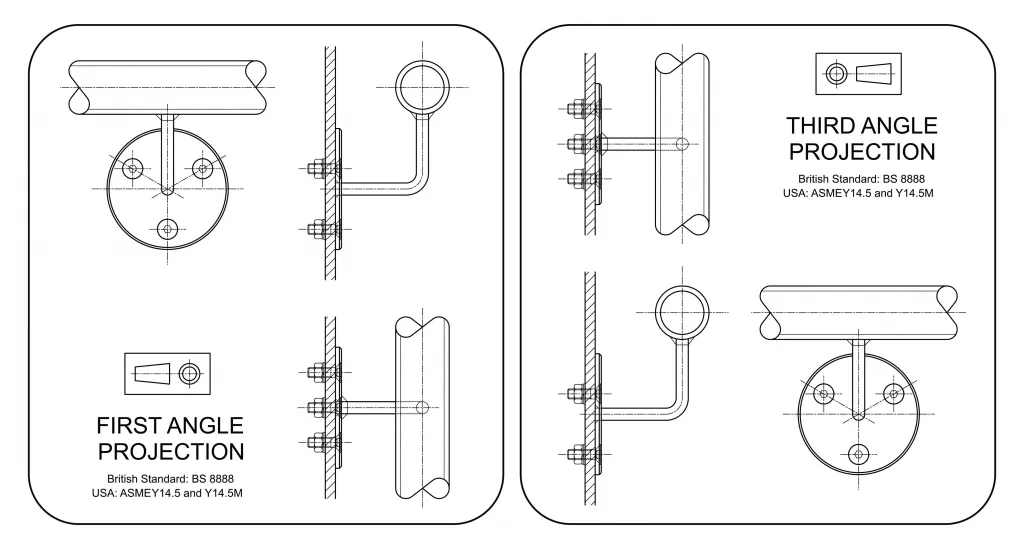
3. Machine Drawing & Fasteners
- Screw Threads: Terms, nomenclature, types, proportions, uses, and thread conventions.
- Nuts & Bolts: Types of nuts, bolts, studs, and locking devices (Machine screws, cap screws, set screws).
- Foundation Bolts: Different types and applications.
- Riveted Joints: Fastening materials, types of rivets, efficiency of joints, and causes of failure.
- Welded Joints: Representation (Actual and Symbolic) and Welding Symbols as per BIS.
4. Mechanical Components & Systems
- Keys, Cotters & Pins: Purpose, types (Heavy/Light duty), and use of cotters and pins.
- Couplings: Necessity, classification, materials, and proportions of different types.
- Bearings: Frictional and anti-frictional bearings (Ball, roller, thrust, needle, and taper roller); materials and properties.
- Power Transmission: Belts (materials, slip, creep, velocity ratio), Pulley ratio, and V-belt drive calculations.
- Gears: Types of gears (Cast vs. Machined), use of Nomographs for drawing gear profiles.
- Cams: Types of cams and followers, displacement diagrams, and kinds of motion.
- Piping: Specifications of W.I. & Steel pipes, pipe threads, and fittings.
5. Advanced Engineering Tools & Principles
- Engines: Brief description of Petrol, Diesel, and Gas engines.
- Hydraulics: Working principle of valves, hydraulic jacks, presses, accumulators, and rams.
- Structural Steel: B.I.S. Specifications for rolled sections, roof truss joints, and supports.
- Measurement: Precision instruments like Vernier height gauges, micrometers, and gauges.
- Limits, Fits & Tolerances: Geometrical tolerance, surface finish symbols (grades and micron values), and IS:919/IS:2709 standards.
Skill Test Syllabus (Practical)
Candidates will be assessed on their ability to perform the following tasks:
- Documentation: Preparing industrial documents and recording information.
- Geometrical Construction: Drawing complex figures using manual instruments.
- Orthographic & Sectional Views: Drawing detailed machine parts with proper title blocks and dimensions.
- CAD Proficiency: * Creating objects in CAD using toolbars, commands, and menus.
- 3D Modeling: Creating 3D objects and converting them to 2D projections.
- Customizing layers, styles, and creating standard templates/callouts.
- Assembly & BOM: Creating part lists and Bill of Materials (BOM) for sub-assemblies.
- Inspection: Measuring components using gauges and checking for accuracy (ISO tolerances).
Strategic Preparation Guide
- BIS Standards: Focus heavily on IS:919 (Tolerances) and IS:2709 (Fits). NSI technical exams often ask specific questions about standard symbols used in drawing.
- CAD Shortcuts: For the Skill Test, master AutoCAD commands (L, O, EX, TR, CO) to save time, as speed is often a qualifying factor.
- Manual Drawing: Don’t neglect manual lettering and scales. At least 20% of the theory marks often come from fundamental drawing instruments and geometry.
- Mechanical Knowledge: Since the eligibility requires a Diploma in Mechanical Engineering, expect detailed questions on Thermal Engineering basics (Engines) and Fluid Mechanics (Hydraulic Jack).
Official Resources
- Official Website: nsi.gov.in
- Recruitment Portal: NSI Career Page
- Application Deadline: March 15, 2026.







