National Sugar Institute (NSI) Syllabus: Research Assistant (Engineering)
Contents
✓ Verified against National Sugar Institute (NSI) Official Advertisement No. 1/2026. All technical and aptitude topics reproduced verbatim.
The National Sugar Institute (NSI), Kanpur, conducts a specialized recruitment process for the post of Research Assistant (Engineering). The examination is divided into two distinct papers designed to test both foundational logic and core engineering expertise at the Diploma level.
Exam Pattern Overview (2026)
| Paper | Type | Subjects | Nature |
| Paper 1 | Written | General Intelligence & Reasoning (Aptitude) | Qualifying Only |
| Paper 2 | Written | Technical Paper (Electrical & Mechanical) | Merit-Ranking |
- Total Marks: 100 (Standard NSI Pattern)
- Duration: 3 Hours (Combined)
- Level: Diploma in Engineering (Electrical & Mechanical)
- Negative Marking: Generally not applicable for qualifying sections (Check specific admit card instructions).
Paper 1: General Intelligence and Reasoning
Note: This paper is of qualifying nature only and marks are not accounted for in the final merit list.
- Quantitative Aptitude: Numerical calculations, percentages, and data interpretation.
- Logical Reasoning: Verbal and non-verbal reasoning, analogies, and classification.
- Aptitude Test: Basic problem-solving and situational judgment.
Paper 2: Written Examination/Technical Paper (100% Verbatim)
The standard of questions is mapped to the Diploma in Engineering (Electrical & Mechanical) curriculum.
1. Electrical Engineering Core
- Basic concepts: Concepts of resistance, inductance, capacitance, and various factors affecting them. Concepts of current, voltage, power, energy and their units.
- Circuit law: Kirchhoff’s law, Simple Circuit solution using network theorems.
- Magnetic Circuit: Concepts of flux, mmf, reluctance, Different kinds of magnetic materials, Magnetic calculations for conductors of different configuration (straight, circular, solenoidal, etc.). Electromagnetic induction, self and mutual induction.
- AC Fundamentals: Instantaneous, peak, R.M.S. and average values of alternating waves, Representation of sinusoidal wave form, simple series and parallel AC Circuits consisting of R.L. and C, Resonance, Tank Circuit. Poly Phase system – star and delta connection, 3 phase power, DC and sinusoidal response of R-L and R-C circuit.
- Measurement and Measuring Instruments: Measurement of power (1 phase and 3 phase, both active and re-active) and energy, 2 wattmeter method of 3 phase power measurement. Measurement of frequency and phase angle. Ammeter and voltmeter (both moving coil and moving iron type), extension of range wattmeter, Multimeters, Megger, Energy meter AC Bridges. Use of CRO, Signal Generator, CT, PT and their uses. Earth Fault detection.
2. Electrical Machines & Power Systems
- D.C. Machine: Construction, Basic Principles of D.C. motors and generators, characteristics, speed control and starting of D.C. Motors. Method of braking motor, Losses and efficiency.
- Transformers: 1 phase and 3 phase transformers – Construction, Principles of operation, equivalent circuit, voltage regulation, O.C. and S.C. Tests, Losses and efficiency. Parallel operation and Auto transformers.
- Induction & Synchronous Motors: 3 phase induction motors, rotating magnetic field, torque-speed characteristics, starting and speed control. Fractional Kilowatt Motors and Single-Phase Induction Motors. Synchronous Machines – Generation of 3 phase e.m.f., armature reaction, voltage regulation, and parallel operation.
- Generation, Transmission and Distribution: Types of power stations, Load factor, diversity factor, demand factor, cost of generation. Power factor improvement, tariffs, types of faults.
- Switchgears & Protection: Rating of circuit breakers, Principles of arc extinction, H.R.C. Fuses, Buchholtz relay, Merz-Price system of protection, Lightning arresters.
- Estimation and Costing: Estimation of lighting scheme, machine installation, and relevant IE rules. Earthing practices.
- Utilization of Electrical Energy: Illumination, Electric heating, welding, Electroplating, and Electric drives.
3. Basic Electronics
- Electronic Devices: Working of P-N Junction diodes, Transistors (NPN and PNP), BJT and JFET. Simple circuits using these devices.
4. Mechanical Engineering Core
- Theory of Machines and Machine Design: Concept of simple machine, Four bar linkage and link motion, Flywheels, Power transmission by belts (V-belts and Flat belts), Clutches (Plate and Conical), Gears (Type, profile, and ratio calculation), Governors, Riveted joint, Cams, Bearings, Friction in collars and pivots.
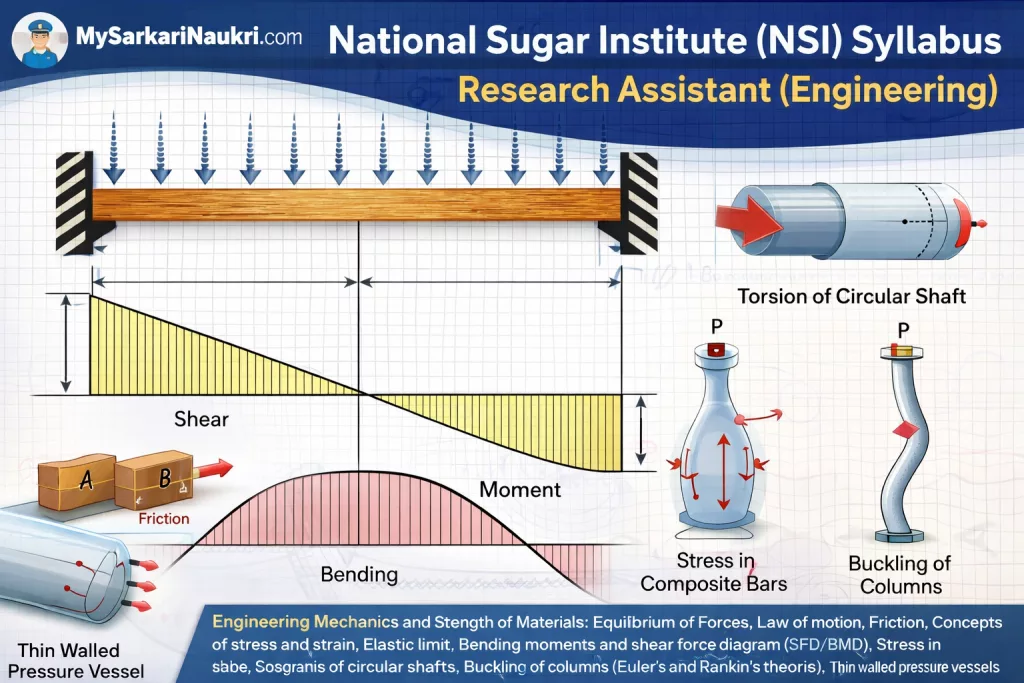
- Engineering Mechanics and Strength of Materials: Equilibrium of Forces, Law of motion, Friction, Concepts of stress and strain, Elastic limit, Bending moments and shear force diagram (SFD/BMD), Stress in composite bars, Torsion of circular shafts, Bucking of columns (Euler’s and Rankin’s theories), Thin walled pressure vessels.
5. Thermal Engineering & Thermodynamics
- Thermal Engineering: Properties of Pure Substances (p-v & P-T diagrams of H₂O), Steam table, saturation, wet & superheated status, dryness fraction, H-s chart (Mollier’s Chart).
- 1st & 2nd Law of Thermodynamics: Cyclic processes, Non-Flow Energy Equation, Steady State Steady Flow Energy Equation (SFEE). Sink, Source, Heat Engine, Heat Pump & Refrigerator (COP). Kelvin-Planck & Clausius Statements, Entropy, Carnot Cycle.
- IC Engines: Air standard Cycles (Otto and Diesel), plot on P-V/T-S planes. Performance, Combustion, Cooling & Lubrication.
- Rankine Cycle & Boilers: Simple Rankine cycle, efficiency calculations. Boilers: Classification (Fire Tube & Water Tube), Specification, Fittings & Accessories.
- Compressors & Refrigeration: Air Compressors & cycles; Principle of a Refrigeration Plant; Nozzles & Steam Turbines.
6. Fluid Mechanics & Production
- Fluid Mechanics: Newton’s law of viscosity, Manometers, Bernoulli’s equation (Total/Velocity/Pressure head), Venturi meter, Pilot tube, Orifice meter. Hydraulic Turbines and Centrifugal Pumps.
- Production Engineering: Classification of Steels, Heat treatment, Welding (Arc, Gas, Resistance, TIG, MIG), Foundry & Casting, Metal cutting principles, Machining (Lathe, Milling, Drilling, Shaping, Grinding).
Strategic Preparation Guide
- Focus on Hybrid Knowledge: Since the paper covers both Electrical and Mechanical topics, candidates often struggle with the “opposite” branch. Use standard Diploma-level textbooks (like R.K. Rajput or B.L. Theraja) for the unfamiliar section.
- IE Rules & Estimation: Do not ignore the “Indian Electricity Rules” and Estimation/Costing; these are specific niche areas often tested in NSI exams.
- Sugar Industry Context: While not explicitly in the technical syllabus, understanding how these machines (Boilers, Pumps, Motors) apply to a sugar refinery can help in the Interview/Skill test phase.
Official Resources
- Official Website: nsi.gov.in
- Application Submission: Registrar/Administrative Officer, National Sugar Institute, Kanpur.
- Notification Reference: Advt No. 1/2026.







